| |
A)
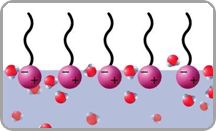
Specialized Surfactants (2)
Work at breaking
down the greases and oils into uniform and small
(head of a pin) size globules. When it has done
that, the surfactant surrounds the soil with a thin
film that repels other globules, thereby not
allowing the grease or oil to recombine into a large
mass. This makes it easier for the water to rinse
away the soil and not allow it to redeposit on the
surface. |
 |
B)
Sequesterant
This is a water
softener that ties up the water minerals so they
will not interfere with the action of the other raw
materials. |
 |
C) Organic Solvents
This
helps to soften hard greases and oils that may have
hardened due to age or temperature. The softer
surfaces are more receptive to the actions of the
other raw materials. |
 |
D)
Alkalis (2)
These
additions work by converting the major components of
greases and oils (fatty acids) into forms of soaps;
thereby, creating another cleaning agent and by
converting a water insoluble soil into a water
soluble cleaner.
|
|
 Safe TileMicro Etching Anti-Slip Solution. Increase traction by creating microscopic channels in most hard mineral surfaces.
Safe TileMicro Etching Anti-Slip Solution. Increase traction by creating microscopic channels in most hard mineral surfaces. WearMaxWaterborne, low VOC, clear anti-slip protective coating system.
WearMaxWaterborne, low VOC, clear anti-slip protective coating system. Multi KleenExtra heavy duty water soluble, green, anti-bacterial, multi–purpose cleaner.
Multi KleenExtra heavy duty water soluble, green, anti-bacterial, multi–purpose cleaner. Safe GripCold vulcanized anti-slip & anti-skid treatment solution. Very fast drying and curing state of the art highly non slip product.
Safe GripCold vulcanized anti-slip & anti-skid treatment solution. Very fast drying and curing state of the art highly non slip product.